The Tragic Story Of Hisashi Ouchi: A Nuclear Accident Warning
Who was Hisashi Ouchi, really? Was he simply a victim of circumstance, or a stark warning against the unseen perils lurking within the nuclear industry? The tragic story of Hisashi Ouchi serves as a chilling testament to the devastating consequences of nuclear accidents and the profound importance of stringent safety protocols.
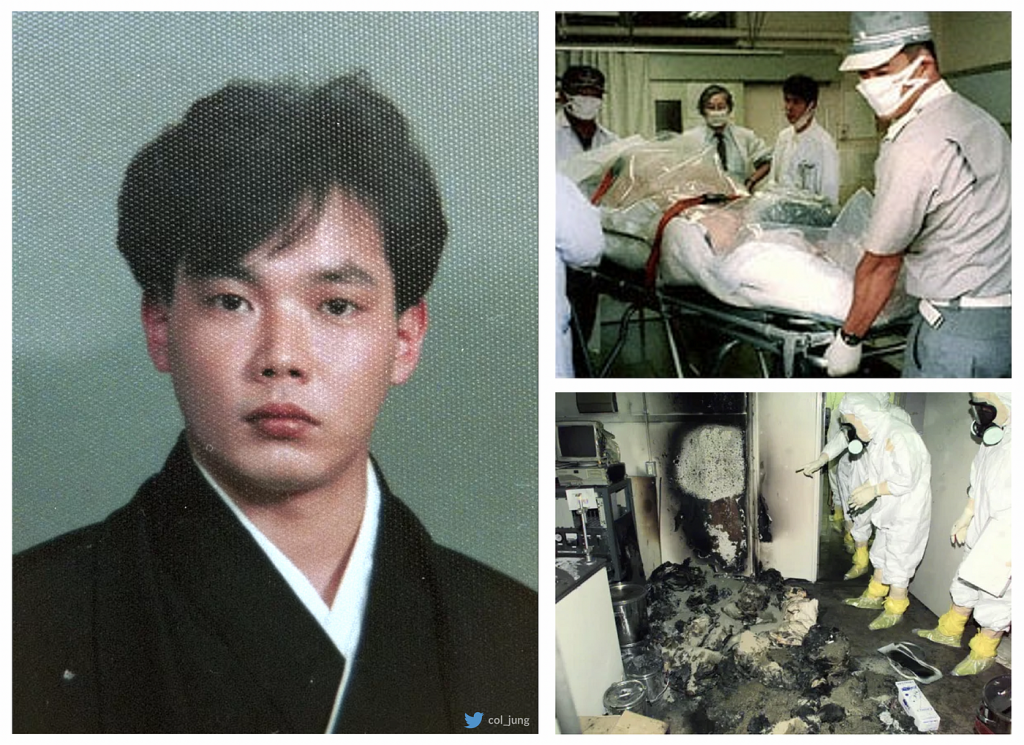
Hisashi Ouchi, a Japanese nuclear technician, became a name synonymous with the unimaginable risks associated with radioactive materials following a criticality accident in 1999. The incident, which occurred at a uranium reprocessing facility in Tokaimura, Japan, resulted in Ouchi's exposure to an extraordinarily high dose of radiation. This exposure inflicted catastrophic damage on his body, leading to his agonizing death three months later, despite the intensive medical interventions he underwent. His case remains one of the most severe and meticulously documented radiation accidents in history, a grim reminder of the potential for devastation when safety measures falter.
The fateful accident unfolded as Ouchi was engaged in the process of preparing a uranium solution. A miscalculation led to the solution reaching criticality, triggering a sudden and intense burst of neutron and gamma radiation. Ouchi, positioned in close proximity to the source, absorbed a lethal dose, initiating a cascade of irreversible biological damage. The event underscores the inherent dangers of working with such volatile materials and the absolute necessity of adhering to rigorous safety standards.
- Enthllt David Rudolf Alter Was Sie Ber Den Anwalt Wissen Mssen
- Neue Infos Ist Kim So Hyun Wirklich Am Daten Gerchte
| Name | Birth Date | Birth Place | Occupation | Date of Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hisashi Ouchi | June 12, 1960 | Ibaraki, Japan | Nuclear technician | December 21, 1999 |
Learn More About Tokaimura Nuclear Accident
In the aftermath of the Tokaimura disaster, a global re-evaluation of safety measures within nuclear facilities took place. While significant improvements have been implemented to mitigate the risk of future incidents, Ouchi's ordeal serves as an unwavering cautionary tale. It underscores the reality that even the most sophisticated safety protocols cannot completely eliminate the potential for human error or unforeseen circumstances. The lessons learned from this tragedy continue to shape nuclear safety practices worldwide.
Hisashi Ouchi's case is a reminder of the dangers of working with radioactive materials.
- Enthllt Pearl Thusi Ehemann Alles Ber Ihre Beziehung
- Alles Ber Justin Pippens Mutter Einfluss Amp Leben Von Glenda Pippen
- Radiation accident
- Nuclear technician
- Criticality accident
- Tokaimura, Japan
- Safety procedures
Hisashi Ouchi's case highlights the importance of safety when working with radioactive materials. Even the most stringent safety measures cannot completely eliminate the risk of accidents. However, by following proper procedures and using proper equipment, the risk of accidents can be minimized.
The narrative of Hisashi Ouchi is one that continues to reverberate within the scientific community and beyond. It is not merely a story of a single accident but a comprehensive illustration of the multiple layers of risk inherent in the nuclear industry. From the initial design and engineering of facilities to the daily routines of technicians, every aspect demands meticulous attention and unwavering commitment to safety. Ouchis suffering serves as a constant reminder of the human cost of complacency or negligence.
The accident in Tokaimura brought into sharp focus the need for enhanced emergency preparedness. While the immediate response to the crisis was commendable, the event revealed gaps in communication, evacuation procedures, and medical readiness. Subsequent reviews emphasized the importance of comprehensive disaster planning that includes not only on-site personnel but also the surrounding communities. Regular drills, simulations, and public awareness campaigns are now recognized as essential components of nuclear safety.
Beyond the immediate aftermath, the Tokaimura accident spurred significant advancements in radiation monitoring and detection technologies. Scientists and engineers worked to develop more sensitive and reliable instruments capable of detecting even minute levels of radiation. These technologies play a crucial role in preventing future accidents by providing early warnings of potential problems and enabling swift corrective actions. Furthermore, research into the biological effects of radiation exposure has intensified, leading to improved treatment protocols for radiation sickness and long-term health monitoring programs for affected individuals.
The human element remains at the core of nuclear safety. Ouchis story underscores the importance of continuous training and education for all personnel working in nuclear facilities. This training must go beyond theoretical knowledge and encompass practical exercises that simulate real-world scenarios. Moreover, fostering a culture of safety where workers feel empowered to raise concerns without fear of reprisal is paramount. Open communication, transparency, and a commitment to continuous improvement are essential ingredients for preventing future tragedies.
The broader implications of the Tokaimura accident extend to the realm of nuclear policy and regulation. Governments around the world have strengthened their oversight of nuclear facilities, implementing stricter licensing requirements, more frequent inspections, and more rigorous enforcement mechanisms. International collaborations, such as those facilitated by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), have also become increasingly important. These collaborations enable the sharing of best practices, the development of common safety standards, and the coordination of emergency response efforts across national borders.
Hisashi Ouchi's legacy is not one of despair but one of enduring vigilance. His sacrifice has fueled a relentless pursuit of safer nuclear technologies and practices. From advanced reactor designs that incorporate inherent safety features to improved waste management strategies that minimize the risk of environmental contamination, the nuclear industry has made significant strides in recent years. However, the lessons learned from Tokaimura must never be forgotten, and the pursuit of excellence in nuclear safety must remain an unwavering priority.
The Tokaimura incident also prompted a deeper examination of the ethical dimensions of nuclear technology. The potential benefits of nuclear power, such as its ability to provide a reliable and low-carbon source of energy, must be weighed against the inherent risks associated with its use. This requires a transparent and inclusive public discourse that involves scientists, policymakers, and citizens. The decisions we make about nuclear technology will have profound implications for future generations, and it is our responsibility to ensure that these decisions are informed by both scientific evidence and ethical considerations.
In addition to the technical and regulatory aspects of nuclear safety, it is also crucial to address the psychological and social impacts of nuclear accidents. The Tokaimura incident had a profound effect on the residents of the surrounding communities, causing widespread fear, anxiety, and distrust. Recovery from such events requires not only physical remediation but also psychological support, community engagement, and a commitment to rebuilding trust. Lessons learned from Tokaimura can inform strategies for mitigating the social and psychological consequences of future nuclear accidents.
Hisashi Ouchi's story is a testament to the resilience of the human spirit. Despite the immense suffering he endured, he remained committed to cooperating with medical professionals and providing valuable insights into the effects of radiation exposure. His contributions to scientific knowledge, made in the face of unimaginable adversity, will continue to benefit future generations. Ouchi's legacy is one of courage, selflessness, and unwavering dedication to the pursuit of knowledge.
The lessons learned from the Tokaimura accident extend beyond the nuclear industry. They have relevance for any organization that handles hazardous materials or engages in high-risk activities. The principles of risk assessment, hazard mitigation, emergency preparedness, and continuous improvement are universally applicable. By studying the Tokaimura case, organizations can identify vulnerabilities in their own systems and take steps to prevent similar tragedies from occurring.
The investigation into the Tokaimura accident revealed a number of contributing factors, including inadequate training, insufficient oversight, and a culture of complacency. These findings underscore the importance of robust management systems that prioritize safety above all else. Organizations must invest in comprehensive training programs, implement rigorous quality control measures, and foster a culture of accountability where employees are empowered to challenge unsafe practices.
The aftermath of the Tokaimura accident also highlighted the importance of international cooperation in nuclear safety. The IAEA played a crucial role in providing technical assistance, coordinating emergency response efforts, and disseminating lessons learned. International collaborations are essential for sharing expertise, developing common safety standards, and ensuring that nuclear facilities around the world operate at the highest levels of safety.
Hisashi Ouchi's case is a powerful reminder of the potential consequences of nuclear accidents. His story has inspired a generation of scientists, engineers, and policymakers to dedicate themselves to improving nuclear safety. By learning from the mistakes of the past, we can work to ensure that nuclear technology is used safely and responsibly for the benefit of all humanity. The pursuit of nuclear safety is a continuous journey, one that requires unwavering commitment, constant vigilance, and a deep respect for the power and the peril of the atom.
A radiation accident is an event that results in the release of radioactive material into the environment. Radiation accidents can have a wide range of consequences, from minor health effects to widespread contamination and death. One of the most severe radiation accidents in history occurred in 1999 at a uranium reprocessing facility in Tokaimura, Japan. A technician named Hisashi Ouchi was working with a uranium solution when it became critical, releasing a burst of radiation. Ouchi was standing close to the solution when it became critical, and he received a lethal dose of radiation.
Ouchi's case highlights the dangers of working with radioactive materials. When an accident occurs, the consequences can be devastating. Radiation accidents can cause a variety of health effects, including radiation sickness, cancer, and death. In addition to the immediate health effects, radiation accidents can also have long-term environmental consequences. Radioactive contamination can persist in the environment for decades or even centuries, and it can pose a health risk to humans and animals.
Radiation accidents are a serious concern, and it is important to take steps to prevent them from occurring. Nuclear facilities should have stringent safety procedures in place, and workers should be properly trained in radiation safety. In addition, it is important to develop new technologies to make nuclear power plants safer and more efficient.
A nuclear technician is a person who works with radioactive materials and nuclear technology. Nuclear technicians are responsible for a variety of tasks, including operating and maintaining nuclear power plants, conducting research on nuclear materials, and developing new nuclear technologies.
Hisashi Ouchi was a nuclear technician who worked at a uranium reprocessing facility in Tokaimura, Japan. In 1999, Ouchi was involved in a criticality accident that released a burst of radiation. Ouchi was standing close to the source of the radiation, and he received a lethal dose. Ouchi's case is a reminder of the dangers of working with radioactive materials.
Nuclear technicians play a vital role in the development and operation of nuclear power plants. However, it is important to remember that working with radioactive materials is dangerous. Nuclear technicians must be properly trained and certified, and they must follow strict safety procedures to minimize the risk of accidents.
The work of nuclear technicians is essential to the safe and efficient operation of nuclear power plants. However, it is important to remember that working with radioactive materials is dangerous. Nuclear technicians must be properly trained and certified, and they must follow strict safety procedures to minimize the risk of accidents.
A criticality accident is an event in which a fissile material becomes self-sustaining, releasing a burst of radiation. Criticality accidents are rare, but they can have devastating consequences. One of the most severe criticality accidents in history occurred in 1999 at a uranium reprocessing facility in Tokaimura, Japan. A technician named Hisashi Ouchi was working with a uranium solution when it became critical, releasing a burst of radiation. Ouchi was standing close to the source of the radiation, and he received a lethal dose.
Criticality accidents are a serious concern, and it is important to take steps to prevent them from occurring. Nuclear facilities should have stringent safety procedures in place, and workers should be properly trained in radiation safety. In addition, it is important to develop new technologies to make nuclear power plants safer and more efficient.
The Tokaimura criticality accident is a reminder of the dangers of working with radioactive materials. Nuclear technicians must be properly trained and certified, and they must follow strict safety procedures to minimize the risk of accidents.
Tokaimura, Japan is a town located in Ibaraki Prefecture, about 120 kilometers northeast of Tokyo. The town is home to the Tokai Reprocessing Plant, a nuclear fuel reprocessing facility. In 1999, a criticality accident occurred at the plant, resulting in the deaths of two workers, including Hisashi Ouchi.
- Location
Tokaimura is located in a rural area of Ibaraki Prefecture. The town is home to about 30,000 people.
- Tokai Reprocessing Plant
The Tokai Reprocessing Plant is a nuclear fuel reprocessing facility. The plant reprocesses spent nuclear fuel from nuclear power plants.
- Criticality accident
In 1999, a criticality accident occurred at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant. The accident resulted in the deaths of two workers, including Hisashi Ouchi.
- Aftermath
The criticality accident at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant had a significant impact on the town of Tokaimura. The accident led to the evacuation of the town and the closure of the plant. The accident also raised concerns about the safety of nuclear power in Japan.
The criticality accident at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant is a reminder of the dangers of nuclear power. The accident also highlights the importance of nuclear safety.
In the wake of the Tokaimura nuclear accident, in which Hisashi Ouchi was fatally irradiated, the importance of stringent safety procedures in nuclear facilities has been brought to the forefront. These procedures are designed to minimize the risk of accidents and protect workers and the public from exposure to radiation.
- Training and certification
Nuclear workers must undergo extensive training and certification to ensure they are properly qualified to handle radioactive materials and operate nuclear equipment.
- Emergency response plans
Nuclear facilities must have comprehensive emergency response plans in place to deal with accidents and minimize their consequences.
- Radiation monitoring
Nuclear facilities must be equipped with radiation monitoring systems to detect and measure radiation levels.
- Security measures
Nuclear facilities must have robust security measures in place to prevent unauthorized access and sabotage.
The strict adherence to safety procedures is paramount to ensuring the safe operation of nuclear facilities and preventing accidents like the one that befell Hisashi Ouchi.
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding the case of Hisashi Ouchi, a Japanese nuclear technician who suffered a criticality accident in 1999.
Question 1: What happened to Hisashi Ouchi?
Hisashi Ouchi was a nuclear technician who was involved in a criticality accident at a uranium reprocessing facility in Tokaimura, Japan, in 1999. The accident exposed him to a lethal dose of radiation, causing severe damage to his body.
Question 2: What is a criticality accident?
A criticality accident occurs when fissile material, such as uranium or plutonium, reaches a critical state, releasing a burst of radiation. This can happen when fissile material is handled improperly or when safety procedures are not followed.
Question 3: How did the accident happen?
The accident occurred when Ouchi and two other technicians were working with a uranium solution. They made a mistake in the process, which caused the solution to become critical. The resulting burst of radiation exposed all three technicians to high levels of radiation.
Question 4: What were the consequences of the accident?
Ouchi received the highest dose of radiation and suffered the most severe injuries. He experienced radiation burns over 100% of his body and damage to his internal organs. Despite receiving intensive medical treatment, he died three months after the accident.
Question 5: What lessons were learned from the accident?
The accident highlighted the importance of following safety procedures when working with radioactive materials. It also led to improvements in safety regulations and training for nuclear workers.
Question 6: What is the legacy of Hisashi Ouchi?
Ouchi's case is a reminder of the dangers of working with radioactive materials. His story has been used to raise awareness about the importance of nuclear safety and to promote better training and safety procedures in nuclear facilities.
The case of Hisashi Ouchi is a tragic reminder of the dangers of nuclear power. It is important to learn from this accident and to take steps to prevent similar accidents from happening in the future.
Learn more about radiation safety and criticality accidents:
- International Atomic Energy Agency: Radiation Safety
- World Nuclear Association: Criticality Accidents
The case of Hisashi Ouchi is a stark reminder of the dangers of nuclear power. Ouchi was a nuclear technician who was involved in a criticality accident in 1999 that exposed him to a lethal dose of radiation. He died three months later after suffering from radiation burns over 100% of his body and damage to his internal organs.
Ouchi's case highlights the importance of following safety procedures when working with radioactive materials. It also shows the need for better training and safety regulations in nuclear facilities. The legacy of Hisashi Ouchi is a reminder that nuclear power is a dangerous technology that must be handled with the utmost care.
Article Recommendations
- George Wads Alles Ber Den Vergessenen Grndervater
- Enthllt David Carradines Beziehungen Eine Turbulente Liebesgeschichte

Detail Author:
- Name : Retta Bechtelar
- Username : kub.dena
- Email : ljaskolski@moore.com
- Birthdate : 1991-01-02
- Address : 2352 Blanche Center Suite 028 East Hector, AK 74398-4655
- Phone : 1-781-700-5985
- Company : White LLC
- Job : Cost Estimator
- Bio : Id qui et odio pariatur unde a quia ut. Facilis nesciunt accusantium quibusdam doloribus omnis perferendis. Veritatis incidunt vel dolor velit. Sit quod quasi ea facere.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/blanca_real
- username : blanca_real
- bio : Corporis libero dolores quam. Et sit quia qui velit.
- followers : 3266
- following : 93
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/fayb
- username : fayb
- bio : Labore voluptas unde fuga est nobis. Officia corrupti autem iusto pariatur quia velit. Maiores provident et dolores quam. Dolor omnis aperiam tempora et.
- followers : 199
- following : 334
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@blanca.fay
- username : blanca.fay
- bio : Nihil reiciendis perspiciatis culpa eum placeat omnis officiis.
- followers : 3449
- following : 1905