Breaking: Does Mark Levin Have Parkinson's? What We Know Now
Is the prominent conservative voice, Mark Levin, battling Parkinson's disease? The speculation swirls, fueled by observations of subtle physical changes, but definitive confirmation remains elusive, leaving many to wonder if the celebrated radio host is facing this formidable neurological challenge.
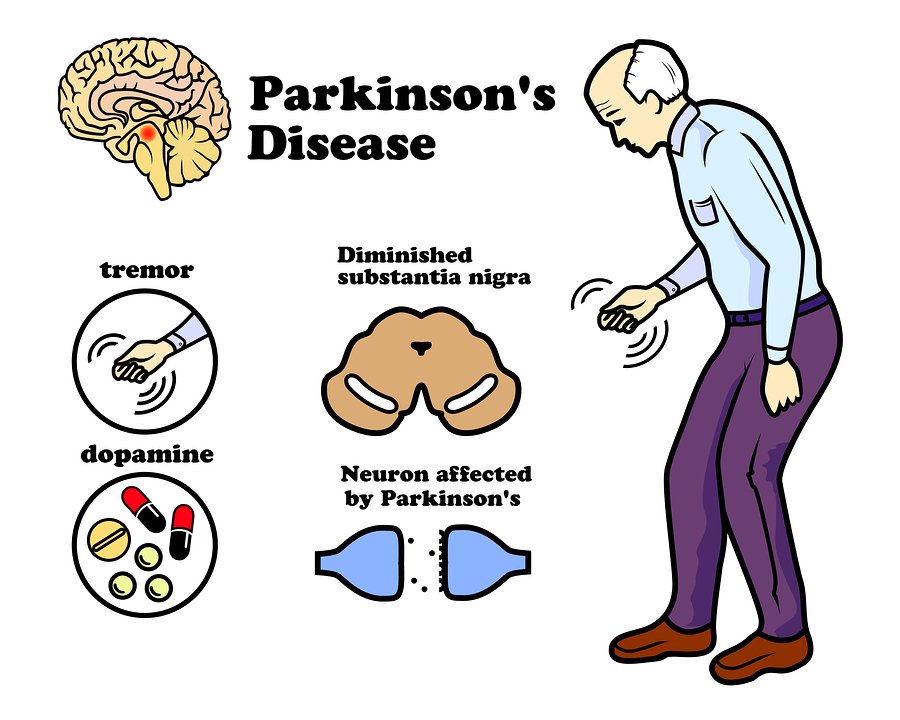
The question of whether Mark Levin, the well-known conservative radio talk show host, is contending with Parkinson's disease has become a topic of considerable discussion, particularly within his listening audience and online communities. Parkinson's disease, a progressive neurological disorder, primarily affects movement, leading to symptoms like tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability. While there's no cure for Parkinson's, a range of medications and therapies can help manage its symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected.
To date, there is no concrete, irrefutable evidence confirming that Mark Levin has been diagnosed with Parkinson's disease. The speculation largely stems from observations made by some individuals who believe they have noticed symptoms consistent with the disease, such as tremors or stiffness, in his public appearances. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that these observations are subjective and do not constitute a medical diagnosis. Mr. Levin himself has neither confirmed nor denied these speculations, maintaining a private stance on his personal health matters.
- Hat Sebastian Maniscalco Wirklich Vorher Geheiratet Das Enthllt
- John Oates Vermgen 2023 So Reich Ist Er Wirklich Geheimnisse
| Name | Born | Occupation | Political party |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mark Levin | September 21, 1957 | Radio talk show host, author, lawyer | Republican |
Should Mark Levin indeed be living with Parkinson's disease, it is conceivable that he is currently in the earlier stages. Parkinson's is characterized by its gradual progression, with symptoms typically evolving over several years. During these initial phases, the manifestations may be subtle and easily overlooked. Nevertheless, even in its nascent stages, Parkinson's can exert a noticeable impact on an individual's daily life, affecting motor skills, energy levels, and overall well-being. Mark Levin Official Website
Considering the possibility, it is important to consider the role of those around him. If friends, family, or observant listeners have genuine concerns about Mark Levin's health, the most constructive course of action would be to encourage him to consult with a medical professional. Early detection and intervention are paramount in managing Parkinson's disease effectively, potentially slowing its progression and maximizing long-term quality of life.
Mark Levin is a conservative radio talk show host who has been accused of having Parkinson's disease. Parkinson's disease is a neurological disorder that affects movement, often causing tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with balance. There is no cure for Parkinson's disease, but medications can help to manage the symptoms.
- Aktuell Warren Brown Hochzeit Alles Ber Die Trauung Des Stars
- Entdecke Jetzt Caroline Keery Mehr Als Nur Ein Star
- Symptoms: Tremors, stiffness, difficulty with balance
- Diagnosis: No definitive evidence, but some symptoms suggest Parkinson's
- Treatment: Medications to manage symptoms
- Prognosis: Parkinson's disease typically progresses slowly
- Impact: Can have a significant impact on quality of life
- Importance of early diagnosis: Can help to slow progression and improve quality of life
- Public interest: Levin is a public figure, so there is interest in his health
If Levin does have Parkinson's disease, it is likely that he is in the early stages of the disease. Parkinson's disease typically progresses slowly, and it can take many years for the symptoms to become severe. However, even in the early stages, Parkinson's disease can have a significant impact on a person's life. It is important to encourage Levin to see a doctor if you are concerned that he may have Parkinson's disease.
The constellation of symptoms associated with Parkinson's diseasetremors, rigidity, and postural instabilitysignificantly disrupts an individual's motor capabilities. These symptoms result from the progressive degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra, a region of the brain responsible for motor control. Dopamine, a critical neurotransmitter, facilitates seamless communication between brain regions involved in movement. The deficiency in dopamine disrupts these pathways, precipitating the characteristic motor impairments of Parkinson's.
- Tremors: Often the most recognizable symptom, tremors in Parkinson's typically manifest as rhythmic shaking, frequently beginning in the hand or fingers. These tremors are often described as "resting tremors," meaning they are most prominent when the limb is at rest and tend to diminish during purposeful movement. The tremor can vary in intensity and may affect one or both sides of the body.
- Stiffness: Rigidity, or stiffness, is another hallmark of Parkinson's disease. It is characterized by an increased resistance to passive movement of the limbs, neck, or trunk. The stiffness can be uniform throughout the range of motion (lead-pipe rigidity) or may present as a ratcheting sensation (cogwheel rigidity). Rigidity contributes to muscle aches, pain, and a general sense of inflexibility.
- Difficulty with balance: Postural instability, or difficulty with balance, arises from the impaired reflexes needed to maintain an upright posture. Individuals with Parkinson's may experience a tendency to lean forward or backward, increasing their risk of falls. Postural instability is often a later-stage symptom, becoming more pronounced as the disease progresses.
Beyond the core motor symptoms, Parkinson's disease can also trigger a spectrum of non-motor symptoms, including cognitive changes, mood disorders (such as depression and anxiety), sleep disturbances, and autonomic dysfunction (affecting blood pressure, bowel function, and bladder control). These non-motor symptoms can significantly impact a person's quality of life, often requiring a multidisciplinary approach to management. If any of these symptoms arise, it is critical to seek medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause and to implement appropriate interventions.
Diagnosing Parkinson's disease is primarily a clinical process, relying on a neurologist's assessment of an individual's medical history, neurological examination, and the presence of cardinal motor symptoms. While there is no single, definitive test for Parkinson's, certain diagnostic tools can aid in the evaluation.
These tools includes:
- Clinical Examination: Neurologists assess motor skills (gait, balance, coordination), reflexes, and sensory function. The presence of tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability are key indicators.
- Medical History: The neurologist will inquire about the onset, duration, and progression of symptoms, as well as any family history of Parkinson's or related disorders.
- Dopamine Transporter Scan (DaTscan): This imaging technique can visualize dopamine activity in the brain. A DaTscan can help differentiate Parkinson's disease from other conditions that mimic its symptoms.
- MRI Scan: While MRI is not used to diagnose Parkinson's, it helps rule out other structural brain abnormalities that could cause similar symptoms.
For Mark Levin, the absence of a public statement regarding a Parkinson's diagnosis necessitates caution in drawing conclusions. The observed symptoms could be attributable to other factors, such as essential tremor, medication side effects, or age-related changes. It is vital to respect Mr. Levin's privacy and await official confirmation before making assumptions about his health. The absence of definitive proof does not necessarily negate the possibility of Parkinson's, as early-stage symptoms can be subtle and may not warrant immediate medical attention.
If a diagnosis of Parkinson's disease is confirmed, prompt access to comprehensive medical care becomes crucial. The cornerstone of Parkinson's management involves medications that aim to replenish dopamine levels in the brain or mimic dopamine's effects.
The main treatment include:
- Levodopa: This medication converts to dopamine in the brain, alleviating motor symptoms. It's often combined with carbidopa to prevent side effects.
- Dopamine Agonists: These drugs mimic dopamine, stimulating dopamine receptors in the brain.
- MAO-B Inhibitors: These medications block the breakdown of dopamine in the brain, extending its effects.
- COMT Inhibitors: These drugs enhance the effectiveness of levodopa by preventing its breakdown.
In addition to medications, lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and participation in support groups, can greatly enhance the quality of life for individuals with Parkinson's.
The link between pharmacological interventions and Mark Levin's situation hinges on the hypothetical scenario of a Parkinson's diagnosis. If Mr. Levin were diagnosed, medication would likely be prescribed to alleviate his symptoms and improve motor function.
The following medications are:
- Dopamine Replacement Therapy: Levodopa, a precursor to dopamine, is converted into dopamine in the brain. Carbidopa is often co-administered to prevent the premature breakdown of levodopa, increasing its effectiveness and reducing side effects such as nausea.
- Dopamine Agonists: These medications mimic the effects of dopamine in the brain, stimulating dopamine receptors. They can be used as monotherapy in early-stage Parkinson's or as an adjunct to levodopa in later stages.
- Monoamine Oxidase B (MAO-B) Inhibitors: These drugs block the enzyme MAO-B, which breaks down dopamine in the brain, thereby increasing dopamine levels. They can be used as monotherapy or in combination with levodopa.
- Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT) Inhibitors: These medications inhibit the COMT enzyme, which breaks down levodopa. By blocking COMT, these inhibitors prolong the duration of levodopa's effects.
These medications can alleviate tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia, and improve overall motor control. However, it's crucial to recognize that these medications can also have side effects. Levodopa, for example, can cause nausea, dyskinesias (involuntary movements), and fluctuations in motor response (wearing-off effect). Dopamine agonists can induce hallucinations, compulsive behaviors, and sleepiness. Close monitoring by a neurologist is essential to optimize medication regimens and mitigate potential side effects. Compliance with prescribed medication schedules is vital for maintaining stable dopamine levels and minimizing symptom fluctuations.
The potential prognosis for Mark Levin, if he were to have Parkinson's disease, is intricately tied to the pace at which the disease evolves. Parkinson's is characterized by its variable rate of progression, which can differ significantly from person to person.
Key aspect of Prognosis
- Variable Progression: The progression of Parkinson's can range from slow and gradual over many years to more rapid, with symptoms advancing more quickly.
- Early Stage Management: In the initial stages, symptoms may be mild and well-controlled with medication and lifestyle adjustments.
- Long-Term Outlook: While there's no cure for Parkinson's, many individuals can live fulfilling lives for years with proper management.
- Importance of Early Intervention: Early detection and treatment can optimize symptom control and slow down the disease's progression.
Early diagnosis and treatment, coupled with proactive lifestyle adjustments, are paramount in mitigating the potential long-term impact of Parkinson's on an individual's well-being. If Mark Levin is indeed living with Parkinson's, early intervention could play a significant role in preserving his quality of life and maintaining his active involvement in his professional and personal pursuits.
The impact of Parkinson's disease on an individual's quality of life is multifaceted, encompassing physical, social, and emotional dimensions. The physical manifestations of the disease can impede daily activities, potentially leading to social isolation and mood disturbances.
Some limitation may occurs:
- Mobility Challenges: Tremors, rigidity, and postural instability can limit mobility, making it difficult to perform routine tasks and activities.
- Social Withdrawal: Visible symptoms and functional limitations can lead to embarrassment and social withdrawal.
- Mood Disturbances: Parkinson's can trigger depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders, impacting emotional well-being.
- Overall Well-being: The cumulative effects of physical, social, and emotional challenges can significantly diminish overall quality of life.
If Mark Levin were to have Parkinson's, seeking appropriate medical and psychosocial support would be essential in managing these challenges and maintaining his overall well-being. There are various resources available to aid those with Parkinson's, including support groups, rehabilitation programs, and counseling services.
Early diagnosis is crucial in Parkinson's for several reasons. It enables the implementation of timely interventions that can slow disease progression, optimize symptom control, and prevent complications. Early diagnosis also empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and future.
Early diagnosis facilitates:
- Slowing Progression: Medications and lifestyle changes can slow the rate at which the disease advances.
- Symptom Management: Timely interventions can improve symptom control, enhancing quality of life.
- Prevention of Complications: Early treatment can prevent falls, injuries, and other complications associated with Parkinson's.
Therefore, if Mark Levin is indeed experiencing early symptoms of Parkinson's, prompt medical evaluation is paramount to ensure the best possible long-term outcome. Early diagnosis can pave the way for proactive management strategies that can significantly enhance his well-being and preserve his functionality.
As a prominent public figure, Mark Levin's health naturally garners attention. This interest stems from his influential role in shaping public discourse and his connection with a wide audience. Moreover, Parkinson's disease is a subject of widespread concern due to its potential to significantly impact individuals and families.
Factors driving public interest
- Public Figure Status: Levin's prominent role in media and politics creates public interest in his well-being.
- Influence on Public Opinion: His views and opinions influence a substantial segment of the population.
- Parkinson's Awareness: Public discourse surrounding Parkinson's raises awareness about the disease and its impact.
The public's concern for Mark Levin's health can serve as a catalyst for raising awareness about Parkinson's disease, encouraging individuals to recognize early symptoms and seek medical attention if needed. Open discussions about the disease can also promote empathy and support for those living with Parkinson's and their families.
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurological condition affecting movement. It arises from the degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the brain, resulting in a range of motor and non-motor symptoms.
Question 1: What are the primary motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease?
Answer: The main motor symptoms include tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability (difficulty with balance).
Question 2: What is the underlying cause of Parkinson's disease?
Answer: The disease stems from the loss of dopamine-producing cells in a specific region of the brain called the substantia nigra.
Question 3: Can Parkinson's disease be cured?
Answer: Currently, there is no cure for Parkinson's disease, but various treatments can manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Question 4: What is the typical prognosis for individuals with Parkinson's disease?
Answer: The prognosis varies widely. While the disease progresses over time, many individuals can maintain active and fulfilling lives with appropriate management.
Question 5: Are there known risk factors for developing Parkinson's disease?
Answer: Risk factors include age, genetic predisposition, exposure to certain environmental toxins, and prior head trauma.
Question 6: How is Parkinson's disease typically diagnosed?
Answer: Diagnosis relies on a neurologist's clinical evaluation, including a review of symptoms, medical history, and neurological examination.
Effective management of Parkinson's disease involves a multidisciplinary approach encompassing medication, lifestyle adjustments, and supportive therapies. If you suspect you may have Parkinson's, consulting a neurologist is crucial for accurate diagnosis and individualized treatment planning.
Living with Parkinson's disease requires a comprehensive approach, integrating medication, lifestyle modifications, and supportive therapies to optimize well-being.
Tip 1: Adhere to your prescribed medication regimen. Medications can alleviate Parkinson's symptoms, such as tremors, stiffness, and mobility challenges. Consistent adherence to the prescribed schedule ensures stable symptom control.
Tip 2: Engage in regular exercise. Exercise improves flexibility, balance, coordination, and overall fitness. Activities like walking, swimming, and targeted exercises can enhance motor skills and well-being.
Tip 3: Maintain a balanced diet. A healthy diet provides essential nutrients, supporting overall health and energy levels. Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Tip 4: Prioritize adequate sleep. Sufficient sleep is essential for physical and cognitive restoration. Establish a consistent sleep routine and create a relaxing bedtime environment.
Tip 5: Implement stress management techniques. Stress can exacerbate Parkinson's symptoms. Incorporate relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to mitigate stress.
Effective management of Parkinson's involves a holistic approach, combining medical interventions with proactive lifestyle choices. By incorporating these strategies, individuals can optimize their well-being and lead fulfilling lives.
Article Recommendations


Detail Author:
- Name : Arden Schmeler IV
- Username : tokon
- Email : abbott.hassie@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1991-02-09
- Address : 1880 Boyer Manor Suite 985 Bertport, OH 71220-8518
- Phone : 936-210-7429
- Company : Flatley-DuBuque
- Job : Short Order Cook
- Bio : Et tempora sapiente veniam expedita quo. Odit eum quibusdam laborum cum iusto ut culpa. Fugit voluptatibus voluptate cum dignissimos alias laudantium. Quasi optio enim odio quam a deleniti.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/bogisichc
- username : bogisichc
- bio : Aliquam qui voluptatem aliquam sequi odio molestiae assumenda quis.
- followers : 5185
- following : 2218
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/bogisichc
- username : bogisichc
- bio : Voluptas esse iste non officiis nesciunt. Maxime qui eaque dignissimos labore a nobis.
- followers : 3369
- following : 464
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/camryn1084
- username : camryn1084
- bio : Vitae modi rerum est.
- followers : 5564
- following : 1917