Unveiling The Hisashi Ouchi Story: The Horrors Of Radiation
Could one single event encapsulate the sheer, terrifying power of uncontrolled radiation? It can, and the tragic ordeal of Hisashi Ouchi serves as the most devastating example, forever etched in the annals of nuclear history, a chilling testament to the consequences when safety protocols fail.
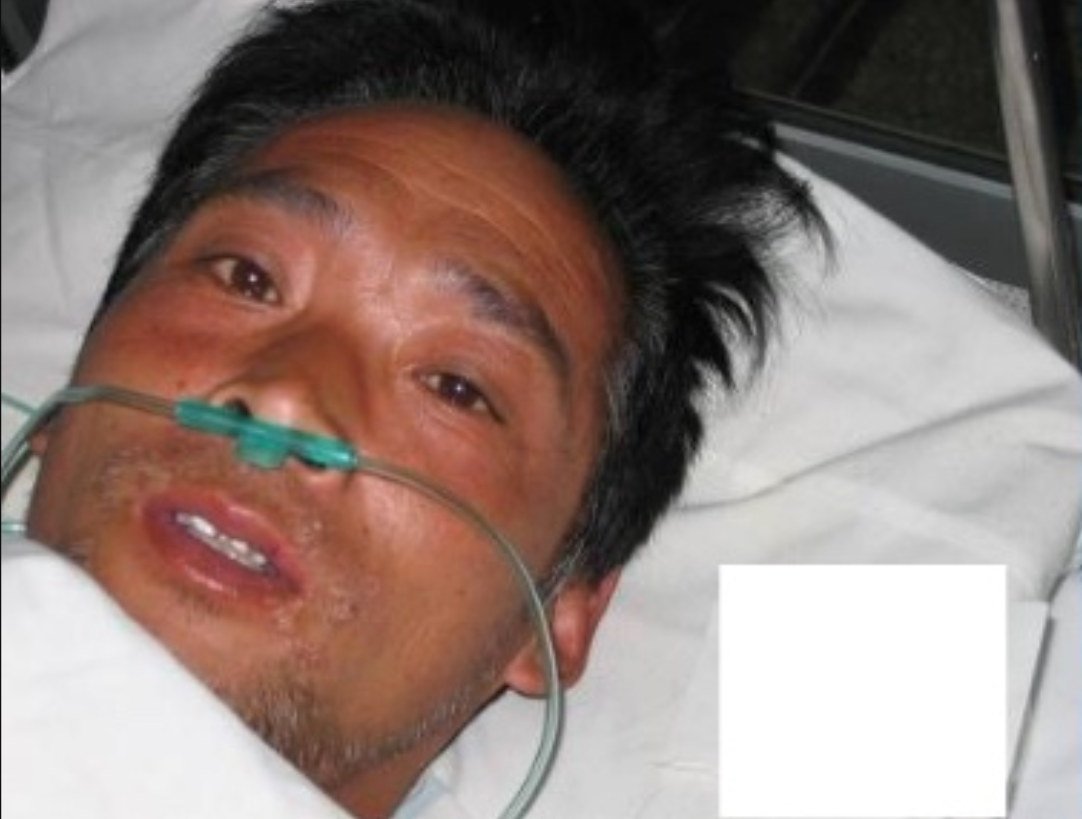
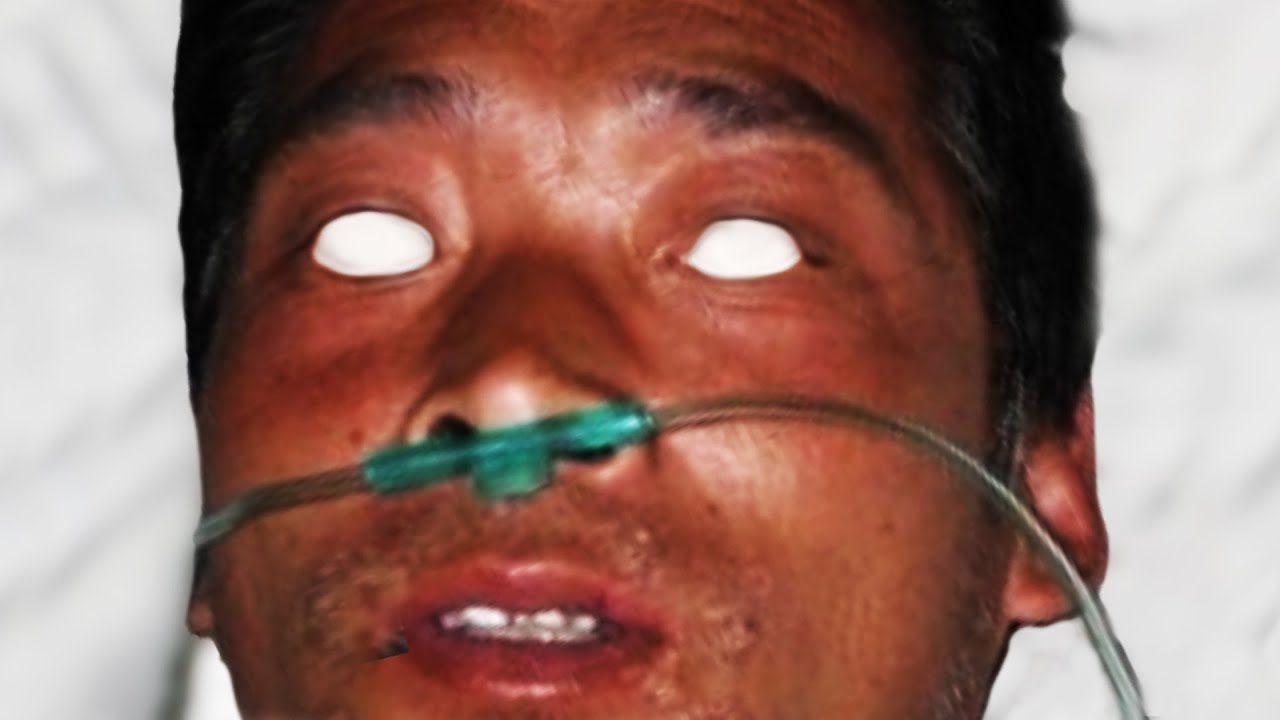
Hisashi Ouchi's name is synonymous with nuclear tragedy. In 1999, while working as a nuclear technician at the Tokaimura Nuclear Power Plant in Japan, Ouchi became the victim of a criticality accident. The sheer magnitude of radiation he absorbed was almost incomprehensible an estimated 17 sieverts (Sv), a figure that dwarfs the accepted lethal dose by more than tenfold. The radiation relentlessly attacked his body, initiating a cascade of catastrophic failures at the cellular level. He succumbed to acute radiation syndrome (ARS), enduring a torturous 83 days before finally succumbing to multiple organ failure. During that time, Ouchi underwent a battery of experimental treatments, including multiple surgeries and skin grafts, none of which could halt the inexorable advance of the radiation's damage. His case became a macabre spectacle, raising profound ethical questions about the limits of medical intervention and the definition of humane treatment in the face of such overwhelming devastation.
Ouchi's suffering, meticulously documented in medical journals and media reports, wasn't just a personal tragedy; it sparked a national crisis in Japan, forcing a long-overdue reckoning with the nation's nuclear power infrastructure. The incident underscored the inherent risks of nuclear technology and the potential for human error to trigger catastrophic events. In the wake of the accident, the Japanese government faced intense public scrutiny and was compelled to overhaul safety regulations at nuclear facilities across the country. These changes included increased investment in radiation monitoring equipment, enhanced worker training programs, and more rigorous enforcement of safety protocols. Furthermore, Ouchi's case triggered a surge in research funding dedicated to understanding the long-term effects of radiation exposure and developing more effective treatments for radiation-induced illnesses.
- Mike Faists Gre So Gro Ist Er Wirklich Seine Karriere
- Exklusive Einblicke Paula Reid Hochzeit Alle Details Amp Hintergrnde
Beyond the immediate aftermath, the story of Hisashi Ouchi resonates as a cautionary tale for the global nuclear industry. It serves as an unflinching reminder that the pursuit of nuclear energy demands an unwavering commitment to safety, transparency, and continuous improvement. Ouchis demise was not in vain, it galvanized the commitment for advanced research in effects of radiation exposure, and it led to the implementation of new safety measures at nuclear power plants around the globe.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Hisashi Ouchi |
| Date of Birth | May 7, 1964 |
| Date of Death | December 21, 1999 |
| Occupation | Nuclear Technician |
| Workplace at the time of accident | Tokaimura Nuclear Power Plant, Japan |
| Cause of Death | Multiple Organ Failure due to Acute Radiation Syndrome |
| Radiation Exposure | Approximately 17 Sieverts (Sv) |
| Legacy | Catalyzed improvements in nuclear safety protocols worldwide, increased research into radiation exposure effects. |
| References | International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) |
Hisashi Ouchi, a Japanese nuclear technician, endured the most severe radiation burns in recorded history in 1999, an ordeal that exposed the profound dangers of radiation and underscored the critical need for robust nuclear safety protocols. Ouchis name is now indelibly linked with this tragic event, a stark illustration of the potential human cost when safety measures falter in the nuclear industry.
- Accident: A criticality accident at a nuclear power plant in 1999, forever changing the landscape of nuclear safety awareness.
- Exposure: Subjected to an astounding 17 sieverts of radiation, exceeding the lethal threshold by a factor of ten.
- Injury: Sustained widespread burns and severe damage to internal organs, leading to systemic failure.
- Treatment: Received multiple surgeries and skin grafts, but his body's regenerative abilities were overwhelmed by the intensity of the radiation damage.
- Death: Succumbed to multiple organ failure three months post-accident, a testament to the body's limits against extreme radiation.
- Legacy: His case became a catalyst for improved nuclear safety measures globally, instigating a new era of caution and proactive protocols.
- Symbol: Embodiment of the catastrophic effects of radiation exposure and the unyielding need for stringent nuclear safeguards.
The case of Hisashi Ouchi serves as both a somber lesson in the perils of radiation exposure and a tribute to the unwavering dedication of the medical professionals who tirelessly sought to alleviate his suffering. Despite their valiant efforts, the sheer extent of Ouchi's injuries rendered recovery impossible, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced preventive measures in nuclear facilities worldwide. The severity of the radiation exposure, coupled with the limitations of existing medical interventions, made Ouchi's survival an insurmountable challenge, underscoring the necessity for stricter safety protocols and technological advancements to minimize the risk of such accidents in the future.
- Alles Ber Mamitha Baiju Ehemann Wer Ist Er Wirklich
- Enthllt Maurice Gibbs Vermgen 2023 So Reich War Das Bee Geesgenie
The criticality accident that occurred at the Tokaimura nuclear power plant in 1999 is intrinsically linked to the harrowing ordeal of Hisashi Ouchi. This single event irrevocably altered his life, setting into motion a series of devastating consequences that ultimately led to his untimely death. The accident stands as a grim milestone in nuclear safety history, highlighting the potential for catastrophic outcomes when safety protocols are breached.
The accident occurred during the processing of uranium fuel at the uranium enrichment facility, where Ouchi and two other workers were performing their duties. A criticality accident, as the name suggests, happens when a fissile material, such as uranium, attains a critical mass, resulting in a self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction. This uncontrolled chain reaction unleashes a powerful surge of radiation, which can be instantly lethal to anyone within its range.
In the Tokaimura incident, the criticality accident was triggered when the workers inadvertently added an excessive amount of uranium to a precipitation tank. This miscalculation caused the uranium to reach a critical mass, initiating a nuclear chain reaction and releasing a flood of radiation. Ouchi and his colleagues were exposed to alarmingly high levels of radiation, far exceeding the permissible limits. Ouchi bore the brunt of the exposure, absorbing an estimated dose of 17 sieverts (Sv), a quantity more than ten times the lethal threshold.
The overwhelming radiation exposure led to the rapid onset of acute radiation syndrome (ARS) in Ouchi. ARS, a condition that wreaks havoc on the body's cells and tissues, presents with a wide array of debilitating symptoms. These symptoms can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, overwhelming fatigue, and significant hair loss. In severe cases, such as Ouchi's, ARS can prove fatal, as the body's vital functions are overwhelmed by the radiation damage. The initial symptoms were just the beginning of a long and agonizing decline for Ouchi, as his body struggled to cope with the immense radiation burden.
Ouchi underwent extensive medical treatment in a desperate attempt to save his life. Medical teams deployed various strategies, but his injuries were simply too extensive. After a protracted struggle of three months, Ouchi succumbed to multiple organ failure, a direct consequence of the severe radiation damage inflicted on his body. His death was a stark reminder of the power of radiation and the fragility of human life in the face of such forces.
The Tokaimura nuclear power plant accident remains a pivotal event, etching itself into history as a testament to the catastrophic potential of radiation exposure. It served as a catalyst for significant changes in the way nuclear power plants are operated, not only in Japan but across the globe. The incident prompted thorough reviews of safety protocols, emergency response plans, and worker training programs to minimize the risk of future accidents.
The astronomical dose of radiation, estimated at approximately 17 sieverts (Sv), that engulfed Hisashi Ouchi, served as the catalyst for his excruciating radiation burns and, ultimately, his death. The lethal dose for humans is typically around 1 Sv, underscoring that Ouchi endured more than ten times the amount necessary to cause fatality. The sheer magnitude of this exposure initiated a cascade of irreversible damage throughout his body, leading to his tragic demise.
Upon exposure, Ouchi developed acute radiation syndrome (ARS), a condition that fundamentally disrupts the normal functioning of the body's cells and tissues. ARS manifests in a range of debilitating symptoms, including severe nausea, persistent vomiting, unrelenting diarrhea, crushing fatigue, and significant hair loss. In severe cases, such as experienced by Ouchi, ARS can lead to death as the body's organ systems are overwhelmed by the radiation's destructive effects. The rapid onset and progression of these symptoms marked the beginning of Ouchi's agonizing struggle.
The immense level of radiation exposure inflicted catastrophic damage on Ouchi's physical form. His skin suffered extensive burns, and his internal organs began a rapid decline. Despite numerous surgeries and skin grafts performed with the aim of mitigating the damage, Ouchi's condition steadily worsened. After fighting for survival for three months, he ultimately succumbed to multiple organ failure, a direct consequence of the high level of radiation to which he was exposed.
The case of Hisashi Ouchi stands as a grim monument to the perils of radiation exposure. The lethal dose of radiation can vary depending on diverse factors, including the type of radiation, the duration of exposure, and the overall health of the individual. However, Ouchi's case starkly illustrates the devastating consequences that can occur when an individual is subjected to an overwhelming dose of radiation. It serves as a somber reminder of the importance of vigilance and adherence to safety protocols in environments where radiation risks are present.
The severe burns and internal organ damage suffered by Hisashi Ouchi were directly precipitated by his exposure to a massive dose of radiation. The radiation exposure caused the breakdown of his cells and tissues, leading to the onset of devastating burns and extensive damage to his internal organs. This cellular and tissue disruption was the root cause of his suffering and eventual demise.
The burns covered the majority of Ouchis body, exceeding 90%, and his internal organs were so profoundly damaged that recovery was not possible. Medical interventions, including multiple surgeries and skin grafts, were undertaken, but his condition continued its downward spiral. His death, resulting from multiple organ failure three months following the incident, was an inevitable consequence of the extensive and irreversible damage caused by the radiation.
The circumstances of Ouchis case provide a stark illustration of the inherent risks involved in radiation exposure. The specific effects of radiation exposure may vary depending on factors such as the type of radiation, the length of exposure, and the individual's underlying health status. However, Ouchi's case provides irrefutable evidence of the devastating consequences that can arise when an individual is subjected to extremely high levels of radiation.
Hisashi Ouchi's medical case presented an unparalleled challenge. The massive radiation exposure he endured triggered extensive burns and internal organ damage. Medical professionals conducted multiple surgeries and skin grafts in an attempt to salvage his life, but unfortunately, his condition continued its downward trajectory. The medical team faced a daunting task in their efforts to combat the effects of such extreme radiation exposure.
- The Severity of Ouchi's Injuries
The intensity of the radiation exposure Ouchi faced resulted in the destruction of his cells and tissues. This destruction manifested in extensive burns and significant internal organ damage. The burns extended over 90% of his body, and the degree of internal organ damage was so severe that recovery was not a viable possibility.
- The Challenges of Treating Radiation Burns
Radiation burns are notoriously challenging to treat due to the damage inflicted on the skin and underlying tissues, hindering the body's natural healing processes. Ouchi's medical team implemented multiple surgeries and skin grafts in the hope of promoting healing, but his condition continued to decline. The complexity of radiation burns made them particularly resistant to conventional medical interventions.
- The Devastating Effects of Radiation Exposure
Ouchi's case serves as a potent reminder of the grave dangers associated with radiation exposure. The radiation exposure resulted in extensive burns and internal organ damage. Despite undergoing numerous surgeries and skin grafts, Ouchi's condition continued to deteriorate, eventually leading to multiple organ failure three months after the initial accident.
Ouchi's story is undeniably tragic, but it underscores the critical importance of maintaining rigorous nuclear safety standards. Nuclear power plants must be operated with unwavering diligence and an uncompromising focus on safety. Furthermore, workers must receive comprehensive training and be provided with the necessary equipment to safely handle radioactive materials. The lessons learned from Ouchi's case should serve as a catalyst for ongoing improvement in nuclear safety protocols.
Hisashi Ouchi, a Japanese nuclear technician, tragically died from multiple organ failure three months after enduring massive radiation exposure in a criticality accident at a nuclear power plant in 1999. His death is a somber reminder of the inherent dangers of radiation exposure and the absolute necessity of maintaining robust nuclear safety practices.
- The Effects of Radiation Exposure
Radiation exposure can trigger a range of serious health issues, including cancer, congenital disabilities, and significant organ damage. The severity of these health effects depends on various factors, such as the extent of radiation exposure, the specific type of radiation involved, and the individual's overall health status.
- Acute Radiation Syndrome
Acute radiation syndrome (ARS) is a condition that can arise after exposure to a high dose of radiation. ARS can manifest in a range of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, and hair loss. In severe instances, ARS can prove fatal, overwhelming the body's ability to function.
- Treatment for Radiation Exposure
Currently, there is no definitive cure for radiation exposure; however, medical interventions can help manage the associated symptoms and improve the patient's overall quality of life. Treatment strategies may include supportive care, such as administering fluids and providing pain management, as well as targeted interventions for ARS symptoms, such as administering antibiotics for infections and providing blood transfusions to address anemia.
- Nuclear Safety
Nuclear power plants must be operated with utmost precision and adherence to strict safety protocols to prevent accidents that could lead to radiation exposure. Workers must receive thorough training and be equipped with the appropriate tools to handle radioactive materials safely. Compliance with safety procedures is paramount.
The untimely death of Hisashi Ouchi is a tragedy, but it also emphasizes the critical importance of adhering to strict nuclear safety standards. Nuclear power plants must be operated with meticulous attention to detail and a steadfast commitment to safety. Workers must be thoroughly trained and equipped to handle radioactive materials safely.
The tragic case of Hisashi Ouchi, the Japanese nuclear technician who endured fatal radiation burns in 1999, has exerted a profound influence on the realm of nuclear safety. His death heightened awareness of the inherent dangers associated with radiation exposure, prompting the implementation of enhanced safety measures across nuclear power plants worldwide. The lessons learned from Ouchi's experience continue to shape and inform nuclear safety practices today.
- Increased public awareness: Ouchi's case brought the potential dangers of radiation exposure to the forefront of public discourse. The extensive media coverage surrounding his case and the subsequent public outcry served to elevate awareness of the potential risks associated with nuclear power and the critical need for robust safety measures.
- Improved safety regulations: In the aftermath of Ouchi's tragic death, nuclear regulatory agencies worldwide undertook comprehensive reviews and strengthened their existing safety regulations. These revised regulations incorporated stricter limitations on radiation exposure for workers, enhanced training mandates, and more robust emergency response protocols.
- Advancements in safety technology: The Ouchi case spurred innovation and development of new safety technologies within nuclear power plants. These technological advancements included enhanced radiation monitoring systems, remotely controlled equipment for handling radioactive materials, and passive safety systems capable of operating without human intervention in the event of an accident.
- International cooperation: Ouchi's death also fostered greater international collaboration and information sharing in the field of nuclear safety. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) played a pivotal role in facilitating the exchange of information and best practices among nuclear power plant operators across the globe.
The legacy of Hisashi Ouchi is one of increased awareness, reinforced safety regulations, and advancements in safety technology. His death has contributed to making nuclear power plants safer and has enhanced the protection of workers and the public from the risks of radiation exposure. His memory serves as a constant reminder of the importance of vigilance and continuous improvement in the nuclear industry.
The ordeal of Hisashi Ouchi, a Japanese nuclear technician who succumbed to fatal radiation burns in 1999, serves as a powerful symbol of the catastrophic effects of radiation exposure and the paramount importance of maintaining robust nuclear safety standards. His case encapsulates the potential dangers inherent in nuclear technology and the need for constant vigilance and improvement.
- A human tragedy: Ouchi's case is a somber reminder of the human toll of radiation exposure. His horrific injuries and subsequent death underscore the immense suffering that can result from nuclear accidents, emphasizing the human element within the complex world of nuclear technology.
- A wake-up call for nuclear safety: Ouchi's death acted as a stark wake-up call for the nuclear industry and regulatory agencies across the globe. It prompted a comprehensive reassessment of existing safety measures and the implementation of more stringent regulations aimed at preventing similar accidents in the future.
- A reminder of the power of radiation: The Ouchi case serves as a potent reminder of the immense power of radiation and the critical need to handle radioactive materials with the utmost care and respect. It emphasizes the potential for devastating consequences if proper safeguards are not in place and strictly followed.
- A call for continued vigilance: Ouchi's death is a constant reminder that nuclear safety is an ongoing process, not a static achievement. We must maintain unwavering vigilance and strive for continuous improvement in our safety measures to avert future tragedies and ensure the responsible use of nuclear technology.
Hisashi Ouchi's case serves as a powerful symbol, reminding us of the devastating consequences of radiation exposure and the unwavering need for nuclear safety. His story must never be forgotten.
The case of Hisashi Ouchi, a Japanese nuclear technician who suffered fatal radiation burns in 1999, raises a series of critical questions regarding radiation exposure and nuclear safety. In an effort to address prevalent concerns and dispel common misconceptions, this FAQ section will delve into various facets of this tragic event.
Question 1: How much radiation was Hisashi Ouchi exposed to?
Ouchi was exposed to approximately 17 sieverts (Sv) of radiation, a quantity exceeding the established lethal dose by more than a factor of ten. This massive radiation exposure inflicted extensive burns and internal organ damage, ultimately resulting in his death three months later. The sheer scale of radiation that Ouchi endured highlights the catastrophic potential of such incidents.
Question 2: What were the symptoms of Ouchi's radiation exposure?
Ouchi experienced a wide range of symptoms as a direct result of his radiation exposure. These symptoms included nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, extreme fatigue, significant hair loss, and severe skin burns. The severity of these symptoms escalated over time, reflecting the progressive nature of his deteriorating condition.
Question 3: What caused Ouchi's death?
Ouchi's death resulted from multiple organ failure, a direct consequence of the extensive radiation damage he sustained during the accident. The massive dose of radiation inflicted severe damage to his internal organs, including his lungs, heart, and digestive system. Despite undergoing intensive medical interventions, his organs were unable to recover from the profound radiation damage, ultimately leading to his demise.
Question 4: What safety measures were in place at the time of the accident?
At the time of the incident, the nuclear power plant where Ouchi worked had implemented a range of safety measures, encompassing radiation monitoring systems, protective clothing, and emergency response procedures. However, the efficacy of these measures proved inadequate in preventing the occurrence of the accident. The shortcomings of these safety measures underscored the need for more robust and comprehensive safety protocols.
Question 5: What lessons were learned from Ouchi's case?
Ouchi's case served as a stark reminder of the necessity for stricter safety measures at nuclear power plants. In the wake of this tragic accident, nuclear regulatory agencies across the globe undertook comprehensive reviews and enhancements of their respective safety regulations. These revised regulations encompassed more stringent limitations on radiation exposure for workers, enhanced training requirements, and more comprehensive emergency response plans.
Question 6: What is the legacy of Hisashi Ouchi?
The legacy of Hisashi Ouchi serves as a poignant reminder of the perils of radiation exposure and the paramount importance of maintaining unwavering nuclear safety standards. His death galvanized increased public awareness regarding the potential risks associated with nuclear power and the critical need for stringent safety measures. The legacy of Ouchi endures through heightened awareness, reinforced safety regulations, and continued advancements in nuclear safety technology.
Summary: The Hisashi Ouchi case serves as a powerful testament to the potential for catastrophic outcomes when dealing with radiation and highlights the critical importance of continuously improving nuclear safety measures. His case is a stark reminder for vigilance and continued vigilance in all areas of nuclear facilities.
Article Recommendations
- Hat Wentworth Miller Wirklich Eine Familie Das Steckt Dahinter
- Die Wahrheit Andrea Brillantes Gre In Fu Warum Es Egal Ist

Detail Author:
- Name : Bell Pouros
- Username : martina.weissnat
- Email : viva.johnson@hane.net
- Birthdate : 1992-05-02
- Address : 938 Crist Vista Suite 668 Gilbertberg, CA 51048
- Phone : 564.299.7527
- Company : Howell Group
- Job : Conveyor Operator
- Bio : Sed est voluptas commodi at omnis. Dicta id aut enim odio ut omnis minus. Iste itaque sed soluta soluta. Molestiae occaecati ab corporis dolor est.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/ignatius5970
- username : ignatius5970
- bio : Ullam sunt ex rem non nisi autem aut nesciunt.
- followers : 2091
- following : 769
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@ignatius_real
- username : ignatius_real
- bio : Eum est laudantium pariatur praesentium dolores optio perferendis.
- followers : 5451
- following : 1707